You are most likely, SEO-savvy and using “white hat” SEO techniques and not losing rank because search engines are penalizing you for using “black hat” SEO techniques. And perhaps you know a little about optimization but not enough to write content that keeps you in the top rankings.
Here are 8 top reasons why your content is not making it to the top and easy remedies to fix these common mistakes.
#1. Lack of relevancy for your keyword
One of the most important factors for determining search ranking is relevancy. Is your content relevant to your keywords?
Every page must have a unique set of meta data and links that create that sense of relevancy. Many websites lack both.
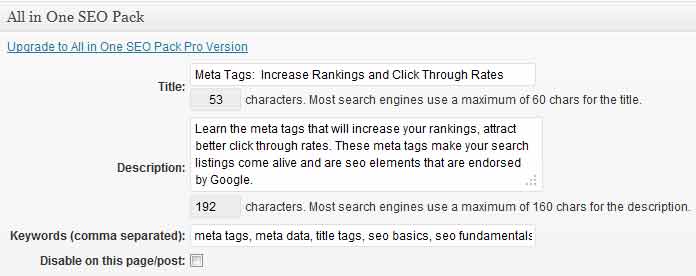
- Meta data relevancy – is your content relevant to the title tag and the description tag you placed on the page? The closer the tags relate to the words used by the searcher and the earlier you use them – in that same order – in the content on the page, the more relevancy your page has.
- Link relevancy – are your links relevant to your content and keywords? The anchor text for links once were also key markers , but now a mix of keyword-rich anchor text and ever more general anchor text linking to still relevant content are more important.
Remedy: Improve content quality with better research, more data, using more links. No one is coming to your site to see you BS your way to a ranking. They want information. Make it your information, written in your voice, with your style and in your tone. Provide links to back up material.
#2. Low keyword use
This probably isn’t as big a problem as keyword stuffing. However, if you use the keyword only once or twice, say at the top of the page, and then ignore it thereafter, you’re probably committing this sin. Don’t over use keywords, but don’t under use them, either. They help make the page relevant.
Remedy: Make your topic clear. Mention your keyword a few times for clarity.
# 3. Irrelevant keyword use (keyword-stuffing)
This is usually a “black hat” SEO trick – stuffing the page with keywords. But sometimes it’s inadvertent. Sometimes it’s from an over abundance of caution. One writer on Technorati suggests we shouldn’t use a keyword more than three times, but search engines would suggest you use it only often enough to serve the reader well – not the search engines. And if you have a high word count, it may make more sense to use it more often than if you have a low word count. Use common sense.
Another sense of “irrelevant keyword use” also comes in the form of trying to fit in all the different varieties of a keyword, just in case someone uses them. Search engines usually differentiate various forms of a word to account for it in a search. Forcing words unnaturally into your content sets off alarms at search engines.
Remedy
- Make better matches between keywords and meta data and meta data placement
- better quality links
- better variety of anchor text for links
- Focus keyword use
#4. Low quality content
Search engines insist, “Write for the reader, not for the search engines.” What pleases the reader more than finding a treasure trove of information? Written in a format that makes it easy to pull out the data.
Poorly written, poorly spelled, poorly constructed content with little value is hard work for the reader and not at all pleasing search engines. Google Panda was also created to weed out low-quality content and that penalty will send your ranking south.
Remedy: Always, aim for high quality content, ie: content that provides value. Try to find topics that have not been indexed by search engines before and that will give you a competitive advantage in rankings. The key is to find a popular topic that has been covered extensively and give your own unique twist to it.
#5. Low word count
Low word count can be one sign of “thin content,” which could trigger the Google Panda penalty.
Longer content helps a search engine determine relevancy. If you provide fewer than 250 words, you may have a problem, although the quality of the text is far more important.
Some websites think shorter word counts are better: “People don’t want to read.” But that’s not true. Readers don’t want to wade through useless text to find value. Shorter sentences and shorter paragraphs aid reader scanning, while meatier content provides them more information – what they really want.
Remedy: A home page under 250 words doesn’t tell the reader much. A blog article of 300-400 words may not provide enough depth. 500-1000 words is a great goal, but write for quality and your audience.
#6. Scraped content (content lifted from other sources)
There is no value to reposting another’s material and you shouldn’t be rewarded for it. It’s lazy publishing, it’s plagiarism, and it’s unethical. You can certainly make “fair use” of short bits of other peoples’ work as a springboard to creating your own larger work, but literal picking up someone else’s work is wrong.
Remedy: Use only original content; use canonical tags in your own content to identify its originality.
#7. Duplicate content
Similarly, running your same material in multiple places on the Internet is wrong. There is a specific penalty for duplicating content. Even replacing a few words here and there doesn’t fool search engines.
Remedy: Don’t duplicate, rewrite! Cover news style with a capsule and link to the original story.
#8. Content you may not generate yourself but may affect your ranking
- Auto-generated text (robotic fluff you sometimes see in comments): Seemingly random sets of words that don’t quite seem to make sense accompanied by strange looking URLs. It’s garbage meant to fool spam filters.
- User-generated spam (comment or forum spam): This is often more sensible text and often written to appeal to your vanity, but sometimes contains spam keywords and certainly spam links. Occasionally, the links lead to OK pages but those pages then link to spam pages, which can negatively affect your ranking.
Remedy:
- Monitor the comments and if something seems odd about a comment, don’t post it. More than likely it’s spam. Post guidelines about spam and police them. Spam and auto-generated text often make off-handed comments that have nothing to do with your topic – delete or send to the spam folder!
- New: Google has just launched a new manual spam notification tool in Webmaster Tools to alert you when your site has been manually tagged for spam. Use it to reduce the effect of spam on your site.